How to Integrate a Ballistic Separator into a Waste Sorting System
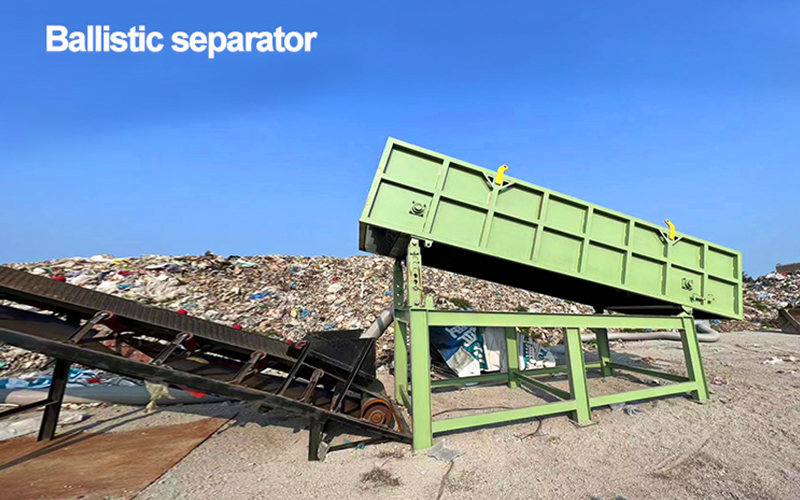

A ballistic separator is a waste-sorting machine that separates materials based on shape,
weight, and density using an inclined oscillating deck. Flat and light materials (like paper)
move upward, while heavy and rolling materials (like bottles) roll downward, enabling efficient
recycling.
Working Principle:
Inclined Oscillating Deck – The machine has a sloped, perforated deck that moves in an
oscillating motion.
Material Movement – Waste materials are fed onto the deck, and the oscillation separates
them based on their behavior:
Flat and Light Materials (like paper and plastic films) stay on top and move upward.
Rolling and Heavy Materials (like cans, bottles, and stones) roll downward.
Fine Materials (like dust and small particles) fall through the perforations.
Final Separation – The materials are directed to different collection areas for further
processing.

Applications:
Municipal Solid Waste (MSW) Sorting – Efficiently separates recyclable materials from
household waste.
Recycling Plants – Enhances material recovery by sorting different waste streams.
Construction and Demolition Waste Processing – Separates heavy debris from reusable
materials.
Packaging Waste Separation – Sorts paper, plastics, and other packaging materials for
recycling.
Advantages:
✔ Efficient Separation of 2D and 3D Materials – Effectively distinguishes between flat
materials (such as paper and plastic film) and rolling or heavy items (such as bottles and
cans), ensuring precise waste segregation.
✔ Low Energy Consumption – Uses mechanical motion instead of air-based separation,
resulting in reduced energy usage and lower operational costs while maintaining high efficiency.
✔ Reduces Manual Sorting Efforts – Automates the separation process, minimizing the
need for human labor, improving workplace safety, and increasing overall processing speed.
How to Integrate a Ballistic Separator into a Waste Sorting System
Placement in the Sorting Line
Position the ballistic separator after the initial pre-sorting (such as shredding or trommel screening) to ensure optimal material separation.
It should be installed before optical sorters, magnetic separators, or manual picking stations to improve sorting efficiency.
Material Feeding
Use a conveyor belt to feed mixed waste into the ballistic separator.
Ensure an even distribution of waste to prevent overloading and maintain consistent separation performance.
Separation Process
The oscillating deck of the separator classifies waste into three fractions:
2D fraction (light, flat materials) – Moves upward for further sorting (e.g., plastics, paper).
3D fraction (heavy, rolling materials) – Rolls downward to another conveyor (e.g., bottles, cans).
Fine fraction (small debris and dust) – Falls through perforations and is collected separately.
Integration with Other Equipment
Optical or Air Separators – Further refine the sorting of plastics and paper from the 2D fraction.
Eddy Current & Magnetic Separators – Extract metals from the 3D fraction.
Manual Sorting – Workers can check and remove contaminants from the output streams.
Control & Monitoring
Set up automated controls to adjust the oscillation speed and deck angle based on waste composition.
Use monitoring systems to track performance and make real-time adjustments for optimal efficiency.
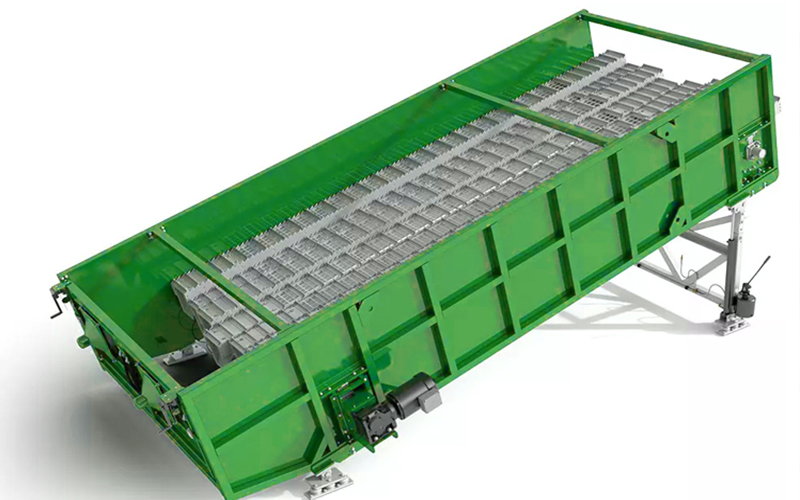
Structure of a Ballistic Separator
Inclined Oscillating Deck
A sloped perforated surface that moves in a controlled oscillating motion to facilitate material separation.
Paddles with Screen Grid Plates
Mounted on rotating shafts, these paddles help classify materials based on shape, size, and weight.
The grid plates are replaceable for different separation needs.
Straight Shafts with Eccentric Bearings
Unique straight shafts equipped with individually exchangeable eccentric bearings to generate the oscillating movement.
Frame and Support Structure
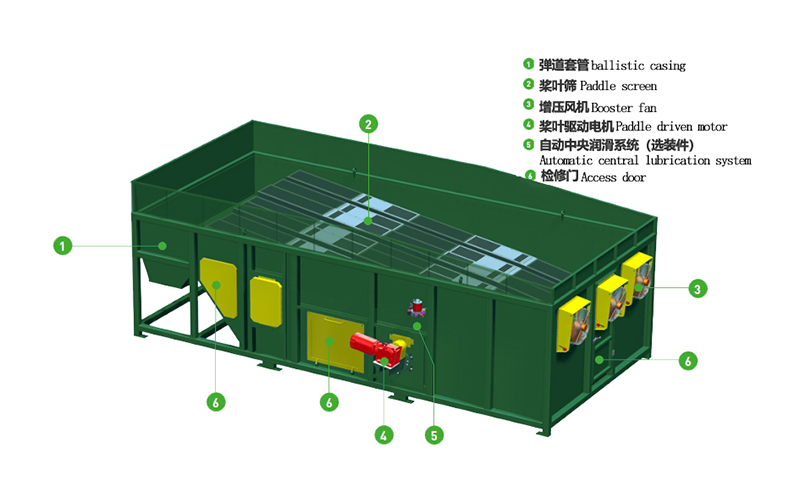
A robust steel frame holds the entire mechanism in place and ensures stability during operation.
Drive System
Includes motors, gears, and eccentric drives that control the oscillating motion of the separator.
Material Discharge Sections
2D (Flat) Material Outlet – Paper, films, and other flat items move upward and are collected separately.
3D (Rolling) Material Outlet – Heavy and rigid materials like bottles and cans roll downward to another conveyor.
Fine Material Outlet – Small debris and dust fall through perforations and are collected below.
Safety Features & Control Panel
Includes sensors, emergency stops, and a user-friendly control panel for efficient operation and monitoring.
Parameters sheet of ballistic separator
| BS04 | BS06 | BS08 | BS10 | BS12 | |
| Paddy Number | 4 | 4 - 6 | 6 - 8 | 6 - 8 | 6 - 10 |
| Paddle length | 5.5m | 5.5m | 5.5m | 5.5m | 5.5m |
| Angle adjustment | 0 – 25° | 0 – 25° | 0 – 25° | 0 – 25° | 0 – 25° |
| Sieve hole size | 20-80 mm | 30-80 mm | 30-80 mm | 30-80 mm | 30-80 mm |
| Fan Number | 2 - 4 | 2 - 4 | 2- 4 | 2 - 4 | 2 - 4 |
| Power | 5.5kw | 7.5kw | 11kw - 15kw | 11kw -18.5kw | 22kw |
| Throughput | 0-30 m³/h | 30-50 m³/h | 50-70 m³/h | 70-90 m³/h | 90-120 m³/h |
-
 Trommel screenTrommel screen, also known as drum screens, are widely used in various industries for sorting and separating materials.Get Quote
Trommel screenTrommel screen, also known as drum screens, are widely used in various industries for sorting and separating materials.Get Quote -
 Crop straw double shaft shreddApplications:Biomass Energy Production: Shredded straw can be used as a feedstock for bioenergy plants to produce electricity or heat.Livestock Feed: Reduced-si...Get Quote
Crop straw double shaft shreddApplications:Biomass Energy Production: Shredded straw can be used as a feedstock for bioenergy plants to produce electricity or heat.Livestock Feed: Reduced-si...Get Quote -
 Zhongcheng Air Drum SeparatorAir drum separators effectively separate lightweight materials (e.g., plastics, paper) from heavier materials (e.g., metals, glass). This high efficiency is cru...Get Quote
Zhongcheng Air Drum SeparatorAir drum separators effectively separate lightweight materials (e.g., plastics, paper) from heavier materials (e.g., metals, glass). This high efficiency is cru...Get Quote
-
2023-01-12Disc ScreenDisc screen, also known as a disc scalping screen, is a mechanical device used to separate materials based on size. It is commonly used in industries such as wa...
-
2024-06-11Optimize Your Waste Management Today with Our Advanced Drum ScreensUnderstanding the Mechanism and Optimization of Drum Screens for Waste Management
-
2024-07-10msw trommel screen for waste recycling machineThis equipment is suitable for the particle classification process in all walks of life:The equipment is simple, easy to operate,and can be operated with a larg...
-
2024-08-22Medical waste shredderWorking Principle:Feeding Mechanism: Medical waste is fed into the shredder through a hopper or chute. The feeding mechanism ensures that the waste is introduce...
-
2024-07-09Recycling Balers-Safe,Easy-To-Use and affordableThe operating principle of a strapping machine primarily involves the following steps:1.Item Positioning:Firstly, the item to be strapped must be placed accurat...



