solid waste incineration
It’s common knowledge that the global accumulation of waste is a long-term environmental threat for
future generations. We haven’t found the perfect way to dispose of all of our waste. There are, however,
existing technologies that allow us to manage our waste more effectively. One of the best examples
of this is responsible solid waste incineration.
how solid waste incinerators work, and how today’s solid waste incineration processes can turn its
byproducts into energy.

Solid Waste Incineration Definition
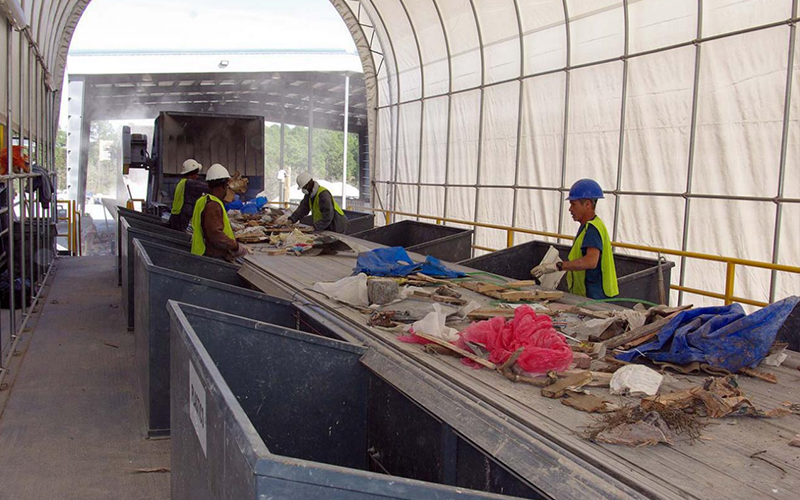
Waste incineration refers to the burning of solid waste at high temperatures in a controlled environment,
which are incinerators. Incinerators are furnaces designed to handle waste materials. This process significantly
reduces the volume of the waste (by up to 95%) and also reduces its mass (by 80-85%).
It's a common method of waste treatment used for various solid waste streams including municipal solid waste
(household trash), medical waste, and some hazardous wastes.

Waste incineration can be a form of waste-to-energy because the heat generated during combustion can be
used to create electricity.

Benefits of Solid Waste Incineration
Waste incineration offers several advantages. Let's check out some key benefits:

Volume Reduction: Incineration significantly reduces the volume of waste by up to 95%. This is quite beneficial in
densely populated areas with limited landfill space.
Energy Recovery: Modern incinerator facilities can be equipped to capture the heat generated during combustion.
This heat can then be used to run turbines and generators that create electric power, providing a form of waste-to-energy
scheme.
Waste Destruction: Incineration can effectively destroy pathogens and harmful toxins in certain waste streams.
This helps to reduce the risk of public health risks and environmental contamination.
Landfill Diversion: By diverting waste from landfills, incineration can help conserve landfill space and reduce the
environmental impact of landfills.
Reduced Reliance on Fossil Fuels: When used for energy generation, waste incineration can partially offset the
need for fossil fuels, potentially leading to lower greenhouse gas emissions. However, this depends on the efficiency
of the incineration process.

Disadvantages of Solid Waste Incineration
While waste incineration has its benefits, there are also significant drawbacks. Here are some key disadvantages:
Air Pollution: Burning waste releases various pollutants into the air such as particulate matter, nitrogen oxides, and
harmful toxins like dioxins. These pollutants can contribute to several health problems.
Ash Disposal: The incineration process does not eliminate waste entirely. It creates ash residue, which can contain
concentrated heavy metals and other toxins. This ash requires careful management and disposal in special landfills.
This disposal adds another layer of complexity.
Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Although incineration can sometimes offset reliance on fossil fuels for energy generation,
it still releases greenhouse gases during the burning process. This can contribute to climate change, especially if the
waste stream contains a lot of plastic.
Disincentive for Reduction and Recycling: Some argue that readily available incineration facilities can discourage efforts
to reduce waste generation and prioritize recycling. If there's a convenient way to burn waste for energy, there might
be a reduction in the focus on waste minimization or recycling.

High Costs: Building and operating incinerator facilities are expensive. The cost of pollution control equipment and
proper ash disposal adds to the overall burden. Here's a ballpark range to give you an idea:

Environmental Justice Concerns: Critics point out that incinerators are often sited in low-income communities or
communities of color, raising concerns about environmental justice and potential disproportionate health impacts on
these populations.

-
 Trommel screenTrommel screen, also known as drum screens, are widely used in various industries for sorting and separating materials.Get Quote
Trommel screenTrommel screen, also known as drum screens, are widely used in various industries for sorting and separating materials.Get Quote -
 Crop straw double shaft shreddApplications:Biomass Energy Production: Shredded straw can be used as a feedstock for bioenergy plants to produce electricity or heat.Livestock Feed: Reduced-si...Get Quote
Crop straw double shaft shreddApplications:Biomass Energy Production: Shredded straw can be used as a feedstock for bioenergy plants to produce electricity or heat.Livestock Feed: Reduced-si...Get Quote -
 Zhongcheng Air Drum SeparatorAir drum separators effectively separate lightweight materials (e.g., plastics, paper) from heavier materials (e.g., metals, glass). This high efficiency is cru...Get Quote
Zhongcheng Air Drum SeparatorAir drum separators effectively separate lightweight materials (e.g., plastics, paper) from heavier materials (e.g., metals, glass). This high efficiency is cru...Get Quote
-
2024-06-05Waste Trommel And Copmost TrommelHowever, it's important to choose the right type of drum screen based on your specific needs. Today, Kevin from Zhongcheng Company will explain the differences...
-
2024-06-05Can the Angle of the Ballistic Separator Be Adjusted?Ballistic separator is a type of mechanical sorting device used primarily in the recycling industry to separate materials based on their physical properties. It...
-
2024-06-07Zhongcheng Air Drum Separator in MSWAir drum separators effectively separate lightweight materials (e.g., plastics, paper) from heavier materials (e.g., metals, glass). This high efficiency is cru...
-
2023-01-12Waste FeederWaste feeder was specially designed to optimize municipal solid waste sorting systems. The Drum Feeder ensures that your sorting system, baler or shredder has a...
-
2023-01-12Disc ScreenDisc screen, also known as a disc scalping screen, is a mechanical device used to separate materials based on size. It is commonly used in industries such as wa...



