How to Set Up a Waste Sorting Facility
Date:2024-09-14
View: Point
Building a waste sorting facility involves several steps, from initial market research to the actual operation. Below is a general process guide:
1. Market Research
- Demand Analysis: Understand the amount and composition of waste generated in your area, as well as the current handling methods.
- Competitive Analysis: Investigate whether there are similar sorting facilities in the region and assess market demand.
- Policy and Regulation Review: Study national and local government policies and regulations regarding waste classification and disposal.
2. Project Planning
- Feasibility Study: Conduct detailed financial projections to evaluate the feasibility and profitability of the project.
- Funding Arrangement: Determine the total investment required for the project and seek funding sources (such as bank loans, government grants, private investments).
- Site Selection: Choose a suitable location for constructing the sorting facility, considering factors like transportation convenience, land costs, and environmental impact.
3. Design and Construction
- Design Plan: Hire professional designers or teams to create an appropriate layout based on the specific waste processing needs.
- Construction Permit: Apply for construction permits from relevant departments to ensure all building activities comply with legal requirements.
- Infrastructure Development: Carry out civil engineering work according to the design plan and install basic facilities such as water and electricity supply, ventilation, fire protection, etc.
4. Equipment Procurement
- Equipment Purchase: Based on the specific needs of waste sorting, purchase the necessary machinery, such as sorting lines, compactors, baling machines, etc.
- Technology Integration: Introduce advanced waste sorting technologies and automation systems to improve work efficiency.
5. Staff Recruitment and Training
- Personnel Configuration: Recruit management personnel, technical staff, operators, etc.
- Pre-employment Training: Train employees on safety operating procedures, equipment usage, and other aspects.
6. Start-up Operations
- Trial Run: Before formal operations begin, conduct a trial run for a period of time to test the performance of the equipment and the rationality of the processes.
- Official Operation: Once everything is ready, officially start the daily operations of the waste sorting facility.
7. Supervision and Maintenance
- Quality Control: Ensure that the sorted waste meets the specified standards.
- Environmental Protection: Implement effective measures to reduce noise, emissions, and other environmental impacts.
- Equipment Maintenance: Regularly inspect and maintain equipment to ensure it operates normally.
8. Publicity and Promotion
- Public Education: Enhance public awareness and support for waste classification through media and community activities.
Partnership Expansion: Establish cooperative relationships with governments, enterprises, non-profit organizations, and others to jointly promote waste classification efforts.
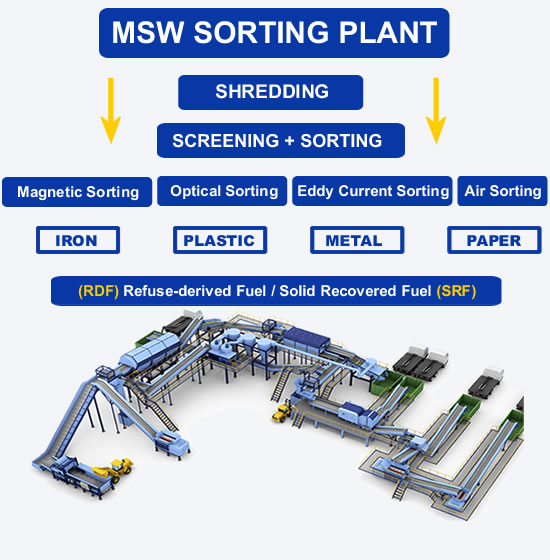
Each step requires detailed planning and execution, and adjustments may be necessary based on actual conditions. Additionally, maintaining good communication with local government authorities throughout the process is crucial to ensure the project proceeds smoothly and receives necessary support.
Zhongcheng Machinery Will Be There Whenever Wherever Whatever You Need
You Are Welcome to : phone call, Message, Wechat, Email& Seaching us, etc.
Email:
sales@zchmachinery.com
Whatsapp/Phone:
+8618738194110
hot Products
-
 Trommel screenTrommel screen, also known as drum screens, are widely used in various industries for sorting and separating materials.Get Quote
Trommel screenTrommel screen, also known as drum screens, are widely used in various industries for sorting and separating materials.Get Quote -
 Crop straw double shaft shreddApplications:Biomass Energy Production: Shredded straw can be used as a feedstock for bioenergy plants to produce electricity or heat.Livestock Feed: Reduced-si...Get Quote
Crop straw double shaft shreddApplications:Biomass Energy Production: Shredded straw can be used as a feedstock for bioenergy plants to produce electricity or heat.Livestock Feed: Reduced-si...Get Quote -
 Zhongcheng Air Drum SeparatorAir drum separators effectively separate lightweight materials (e.g., plastics, paper) from heavier materials (e.g., metals, glass). This high efficiency is cru...Get Quote
Zhongcheng Air Drum SeparatorAir drum separators effectively separate lightweight materials (e.g., plastics, paper) from heavier materials (e.g., metals, glass). This high efficiency is cru...Get Quote
relate news
-
2024-08-07Efficient Material Separation with Bounce ScreensThe ballistic separator is an important equipment with separation function designed for the sorting of inorganic particles in the coarsely crushed waste.
-
2024-07-12Crush to Create: The Ultimate Eco-Friendly Plastic Shredder RevolutionThe working principle of a plastic shredder is mainly to tear large plastic materials into small pieces or fragments through mechanical force, in order to facil...
-
2023-01-12Waste FeederWaste feeder was specially designed to optimize municipal solid waste sorting systems. The Drum Feeder ensures that your sorting system, baler or shredder has a...
-
2024-06-20Wind Separator Technology for Lightweight Materials in Urban Solid Wastewind separator, also known as air separation, is a sophisticated and efficient method of sorting that utilizes air as the separating medium.
-
2023-01-11Ballistic SeparatorBallistic separators are a crucial component in modern recycling and waste management systems, contributing to more efficient resource recovery and environmenta...



